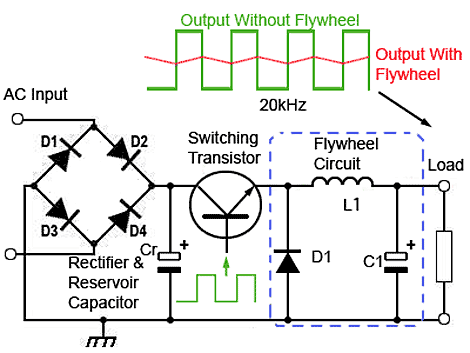
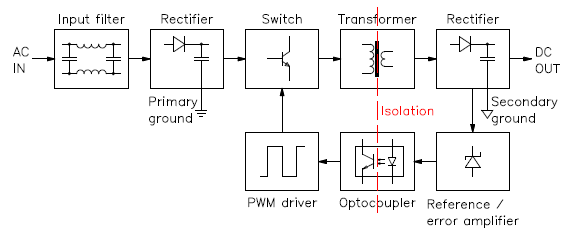
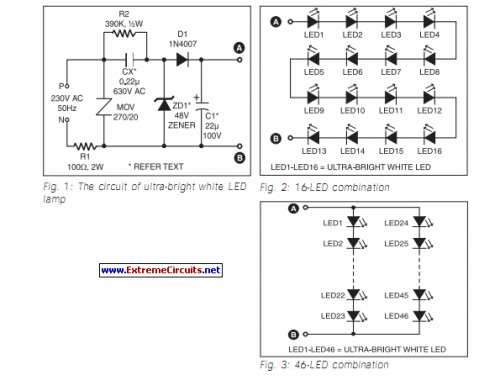
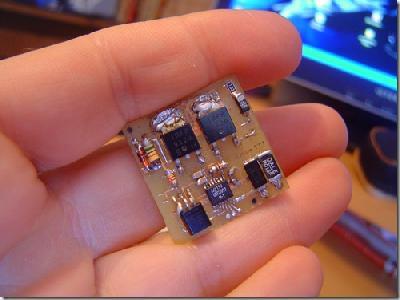
So let’s say you have this digital camera that can take pictures and videos as well, cool eh? But there’s a catch, its battery drains electricity charge fast. The solution, use an external battery, but the hassle of using external batteries is that most of the batteries are 12 volts. So you have to reduce the power voltage as your device gains charge from the higher voltage battery.
This project is also helpful in cars. We can use a USB adapter and convert a 12 volt to a 5 volt transformer. This are great when you charge devices that only requires a little let say like 5 volts digital cameras, cellular phones and tablets. If you need 5 volts for anything other than USB, simply skip the steps about adding the USB ports.
Here are the things that you will need:
- a fuse holder
- a 0.5 amp fast blowing fuse (you can use a higher rated one if you use a different transistor that can take higher amperage. Because we put the fuse on the 12v side, (which can vary from 11.5-12.5 volts, we have to use a value 2.5x smaller than what we want on our USB side. So, if you want 1.5 amps for your USB ports, then you select a 0.6amp fuse, if you want 2.5 amps at 5v, you select a 1 amp fuse, if you want 3.75 amps, you select a 1.5 amp fuse, etc.)
- 2 different colors of wire (so that you don’t get confused later on)
- a L7805CV voltage regulator, part number 497-1443-5-ND from Digikey (search for 296-11414-5-ND if you want higher AMP output, like 2 amps since it is a max of 3 amps along with a 1-1.2 amp fast blowing fuse, and LT1084CT-5#PBF-ND if you want 2 ports at 2 amps each, along with a 1.5-1.75 amp fast blowing fuse.)
- a 220uf 16v Capacitor, part number P5139-ND from Digikey.
- female USB ports times the number of ports you want (2-3 would be normal, you can expect most devices to use up to 0.5A each, except for tablets that can use 1-2 amps), Digikey number AE9923-ND
- if you choose to add an LED, you need an LED and an appropriate resistor for 5V. This depends on your LED’s rating. Any LED will do, here are the values for the most common LEDs : 1.2v = 220ohm, 1.6v = 180ohm, 2v = 180 ohm, 2.2v = 150ohm. If you have a strange LED or want to make it brighter, please use this resistor calculator.
Conclusion
It is always helpful when you have a simple 12v to 5v converter, when you are on the road for a little vacation, charging small devices as never been so easy.
Check out the original post